 |
Qt 4.8
|
 |
Qt 4.8
|
The QNetworkSession class provides control over the system's access points and enables session management for cases when multiple clients access the same access point. More...
#include <qnetworksession.h>
Public Types | |
| enum | SessionError { UnknownSessionError = 0, SessionAbortedError, RoamingError, OperationNotSupportedError, InvalidConfigurationError } |
| This enum describes the session errors that can occur. More... | |
| enum | State { Invalid = 0, NotAvailable, Connecting, Connected, Closing, Disconnected, Roaming } |
| This enum describes the connectivity state of the session. More... | |
Public Slots | |
| void | accept () |
| Instructs the session to permanently accept the new access point. More... | |
| void | close () |
| Decreases the session counter on the associated network configuration. More... | |
| void | ignore () |
| This function indicates that the application does not wish to roam the session. More... | |
| void | migrate () |
| Instructs the session to roam to the new access point. More... | |
| void | open () |
| Creates an open session which increases the session counter on the underlying network interface. More... | |
| void | reject () |
| The new access point is not suitable for the application. More... | |
| void | stop () |
| Invalidates all open sessions against the network interface and therefore stops the underlying network interface. More... | |
 Public Slots inherited from QObject Public Slots inherited from QObject | |
| void | deleteLater () |
| Schedules this object for deletion. More... | |
Signals | |
| void | closed () |
| This signal is emitted when the network session has been closed. More... | |
| void | error (QNetworkSession::SessionError) |
| This signal is emitted after an error occurred. More... | |
| void | newConfigurationActivated () |
| This signal is emitted once the session has roamed to the new access point. More... | |
| void | opened () |
| This signal is emitted when the network session has been opened. More... | |
| void | preferredConfigurationChanged (const QNetworkConfiguration &config, bool isSeamless) |
| This signal is emitted when the preferred configuration/access point for the session changes. More... | |
| void | stateChanged (QNetworkSession::State) |
| This signal is emitted whenever the state of the network session changes. More... | |
 Signals inherited from QObject Signals inherited from QObject | |
| void | destroyed (QObject *=0) |
| This signal is emitted immediately before the object obj is destroyed, and can not be blocked. More... | |
Public Functions | |
| quint64 | activeTime () const |
| Returns the number of seconds that the session has been active. More... | |
| quint64 | bytesReceived () const |
| Returns the amount of data received in bytes; otherwise 0. More... | |
| quint64 | bytesWritten () const |
| Returns the amount of data sent in bytes; otherwise 0. More... | |
| QNetworkConfiguration | configuration () const |
| Returns the QNetworkConfiguration that this network session object is based on. More... | |
| SessionError | error () const |
| Returns the type of error that last occurred. More... | |
| QString | errorString () const |
| Returns a human-readable description of the last device error that occurred. More... | |
| QNetworkInterface | interface () const |
| Returns the network interface that is used by this session. More... | |
| bool | isOpen () const |
| Returns true if this session is open. More... | |
| QNetworkSession (const QNetworkConfiguration &connConfig, QObject *parent=0) | |
| Constructs a session based on connectionConfig with the given parent. More... | |
| QVariant | sessionProperty (const QString &key) const |
| Returns the value for property key. More... | |
| void | setSessionProperty (const QString &key, const QVariant &value) |
| Sets the property value on the session. More... | |
| State | state () const |
| Returns the state of the session. More... | |
| bool | waitForOpened (int msecs=30000) |
| Waits until the session has been opened, up to msecs milliseconds. More... | |
| virtual | ~QNetworkSession () |
| Frees the resources associated with the QNetworkSession object. More... | |
 Public Functions inherited from QObject Public Functions inherited from QObject | |
| bool | blockSignals (bool b) |
| If block is true, signals emitted by this object are blocked (i.e., emitting a signal will not invoke anything connected to it). More... | |
| const QObjectList & | children () const |
| Returns a list of child objects. More... | |
| bool | connect (const QObject *sender, const char *signal, const char *member, Qt::ConnectionType type=Qt::AutoConnection) const |
| bool | disconnect (const char *signal=0, const QObject *receiver=0, const char *member=0) |
| bool | disconnect (const QObject *receiver, const char *member=0) |
| void | dumpObjectInfo () |
| Dumps information about signal connections, etc. More... | |
| void | dumpObjectTree () |
| Dumps a tree of children to the debug output. More... | |
| QList< QByteArray > | dynamicPropertyNames () const |
| Returns the names of all properties that were dynamically added to the object using setProperty(). More... | |
| virtual bool | event (QEvent *) |
| This virtual function receives events to an object and should return true if the event e was recognized and processed. More... | |
| virtual bool | eventFilter (QObject *, QEvent *) |
| Filters events if this object has been installed as an event filter for the watched object. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | findChild (const QString &aName=QString()) const |
| Returns the child of this object that can be cast into type T and that is called name, or 0 if there is no such object. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| QList< T > | findChildren (const QString &aName=QString()) const |
| Returns all children of this object with the given name that can be cast to type T, or an empty list if there are no such objects. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| QList< T > | findChildren (const QRegExp &re) const |
| bool | inherits (const char *classname) const |
| Returns true if this object is an instance of a class that inherits className or a QObject subclass that inherits className; otherwise returns false. More... | |
| void | installEventFilter (QObject *) |
| Installs an event filter filterObj on this object. More... | |
| bool | isWidgetType () const |
| Returns true if the object is a widget; otherwise returns false. More... | |
| void | killTimer (int id) |
| Kills the timer with timer identifier, id. More... | |
| virtual const QMetaObject * | metaObject () const |
| Returns a pointer to the meta-object of this object. More... | |
| void | moveToThread (QThread *thread) |
| Changes the thread affinity for this object and its children. More... | |
| QString | objectName () const |
| QObject * | parent () const |
| Returns a pointer to the parent object. More... | |
| QVariant | property (const char *name) const |
| Returns the value of the object's name property. More... | |
| Q_INVOKABLE | QObject (QObject *parent=0) |
| Constructs an object with parent object parent. More... | |
| void | removeEventFilter (QObject *) |
| Removes an event filter object obj from this object. More... | |
| void | setObjectName (const QString &name) |
| void | setParent (QObject *) |
| Makes the object a child of parent. More... | |
| bool | setProperty (const char *name, const QVariant &value) |
| Sets the value of the object's name property to value. More... | |
| void | setUserData (uint id, QObjectUserData *data) |
| bool | signalsBlocked () const |
| Returns true if signals are blocked; otherwise returns false. More... | |
| int | startTimer (int interval) |
| Starts a timer and returns a timer identifier, or returns zero if it could not start a timer. More... | |
| QThread * | thread () const |
| Returns the thread in which the object lives. More... | |
| QObjectUserData * | userData (uint id) const |
| virtual | ~QObject () |
| Destroys the object, deleting all its child objects. More... | |
Protected Functions | |
| virtual void | connectNotify (const char *signal) |
| This function is required to detect whether the client wants to control the roaming process. More... | |
| virtual void | disconnectNotify (const char *signal) |
| This function is called when the client disconnects from the preferredConfigurationChanged() signal. More... | |
 Protected Functions inherited from QObject Protected Functions inherited from QObject | |
| virtual void | childEvent (QChildEvent *) |
| This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive child events. More... | |
| virtual void | customEvent (QEvent *) |
| This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive custom events. More... | |
| QObject (QObjectPrivate &dd, QObject *parent=0) | |
| int | receivers (const char *signal) const |
| Returns the number of receivers connected to the signal. More... | |
| QObject * | sender () const |
| Returns a pointer to the object that sent the signal, if called in a slot activated by a signal; otherwise it returns 0. More... | |
| int | senderSignalIndex () const |
| virtual void | timerEvent (QTimerEvent *) |
| This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive timer events for the object. More... | |
Properties | |
| QNetworkSessionPrivate * | d |
Friends | |
| class | QNetworkSessionPrivate |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Static Public Functions inherited from QObject Static Public Functions inherited from QObject | |
| static bool | connect (const QObject *sender, const char *signal, const QObject *receiver, const char *member, Qt::ConnectionType=Qt::AutoConnection) |
| Creates a connection of the given type from the signal in the sender object to the method in the receiver object. More... | |
| static bool | connect (const QObject *sender, const QMetaMethod &signal, const QObject *receiver, const QMetaMethod &method, Qt::ConnectionType type=Qt::AutoConnection) |
| static bool | disconnect (const QObject *sender, const char *signal, const QObject *receiver, const char *member) |
| Disconnects signal in object sender from method in object receiver. More... | |
| static bool | disconnect (const QObject *sender, const QMetaMethod &signal, const QObject *receiver, const QMetaMethod &member) |
| static uint | registerUserData () |
| static QString | tr (const char *sourceText, const char *comment=0, int n=-1) |
| static QString | trUtf8 (const char *sourceText, const char *comment=0, int n=-1) |
 Static Public Variables inherited from QObject Static Public Variables inherited from QObject | |
| static const QMetaObject | staticMetaObject |
| This variable stores the meta-object for the class. More... | |
 Protected Variables inherited from QObject Protected Variables inherited from QObject | |
| QScopedPointer< QObjectData > | d_ptr |
 Static Protected Variables inherited from QObject Static Protected Variables inherited from QObject | |
| static const QMetaObject | staticQtMetaObject |
 Related Functions inherited from QObject Related Functions inherited from QObject | |
| T | qFindChildqFindChildren (const QObject *obj, const QString &name)() |
| QList< T > | qFindChildrenqFindChildren (const QObject *obj, const QString &name)() |
| QList< T > | qFindChildrenqFindChildren (const QObject *obj, const QRegExp ®Exp)() |
| T * | qobject_cast (QObject *object) |
| QObjectList | |
| void * | qt_find_obj_child (QObject *parent, const char *type, const QString &name) |
| Returns a pointer to the object named name that inherits type and with a given parent. More... | |
The QNetworkSession class provides control over the system's access points and enables session management for cases when multiple clients access the same access point.
A QNetworkSession enables control over the system's network interfaces. The session's configuration parameter are determined via the QNetworkConfiguration object to which it is bound. Depending on the type of the session (single access point or service network) a session may be linked to one or more network interfaces. By means of opening and closing of network sessions a developer can start and stop the systems network interfaces. If the configuration represents multiple access points (see QNetworkConfiguration::ServiceNetwork ) more advanced features such as roaming may be supported.
QNetworkSession supports session management within the same process and depending on the platform's capabilities may support out-of-process sessions. If the same network configuration is used by multiple open sessions the underlying network interface is only terminated once the last session has been closed.
Applications may connect to the preferredConfigurationChanged() signal in order to receive notifications when a more suitable access point becomes available. In response to this signal the application must either initiate the roaming via migrate() or ignore() the new access point. Once the session has roamed the newConfigurationActivated() signal is emitted. The application may now test the carrier and must either accept() or reject() it. The session will return to the previous access point if the roaming was rejected. The subsequent state diagram depicts the required state transitions.
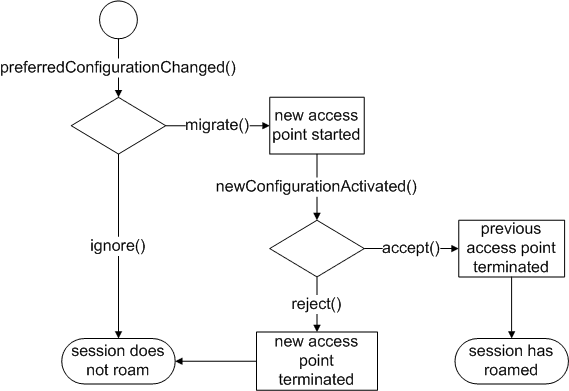
Some platforms may distinguish forced roaming and application level roaming (ALR). ALR implies that the application controls (via migrate(), ignore(), accept() and reject()) whether a network session can roam from one access point to the next. Such control is useful if the application maintains stateful socket connections and wants to control the transition from one interface to the next. Forced roaming implies that the system automatically roams to the next network without consulting the application. This has the advantage that the application can make use of roaming features without actually being aware of it. It is expected that the application detects that the underlying socket is broken and automatically reconnects via the new network link.
If the platform supports both modes of roaming, an application indicates its preference by connecting to the preferredConfigurationChanged() signal. Connecting to this signal means that the application wants to take control over the roaming behavior and therefore implies application level roaming. If the client does not connect to the preferredConfigurationChanged(), forced roaming is used. If forced roaming is not supported the network session will not roam by default.
Some applications may want to suppress any form of roaming altogether. Possible use cases may be high priority downloads or remote services which cannot handle a roaming enabled client. Clients can suppress roaming by connecting to the preferredConfigurationChanged() signal and answer each signal emission with ignore().
Definition at line 71 of file qnetworksession.h.
This enum describes the session errors that can occur.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| UnknownSessionError | |
| SessionAbortedError | |
| RoamingError | |
| OperationNotSupportedError | |
| InvalidConfigurationError | |
Definition at line 86 of file qnetworksession.h.
This enum describes the connectivity state of the session.
If the session is based on a single access point configuration the state of the session is the same as the state of the associated network interface.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| Invalid | |
| NotAvailable | |
| Connecting | |
| Connected | |
| Closing | |
| Disconnected | |
| Roaming | |
Definition at line 76 of file qnetworksession.h.
|
explicit |
Constructs a session based on connectionConfig with the given parent.
Definition at line 261 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QSharedNetworkSessionManager::getSession().
|
virtual |
Frees the resources associated with the QNetworkSession object.
Definition at line 294 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
|
slot |
Instructs the session to permanently accept the new access point.
Once this function has been called the session may not return to the old access point.
The old access point may be closed in the process if there are no other network sessions for it. Therefore any open socket that still uses the old access point may become unusable and should be closed before completing the migration.
Definition at line 630 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkSessionPrivate::setALREnabled().
| quint64 QNetworkSession::activeTime | ( | ) | const |
Returns the number of seconds that the session has been active.
Definition at line 691 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkSessionPrivate::setALREnabled().
| quint64 QNetworkSession::bytesReceived | ( | ) | const |
Returns the amount of data received in bytes; otherwise 0.
This field value includes the usage across all open network sessions which use the same network interface.
If the session is based on a service network configuration the number of sent bytes across all active member configurations are returned.
This function may not always be supported on all platforms and returns 0. The platform capability can be detected via QNetworkConfigurationManager::DataStatistics.
Definition at line 683 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkSessionPrivate::setALREnabled().
| quint64 QNetworkSession::bytesWritten | ( | ) | const |
Returns the amount of data sent in bytes; otherwise 0.
This field value includes the usage across all open network sessions which use the same network interface.
If the session is based on a service network configuration the number of sent bytes across all active member configurations are returned.
This function may not always be supported on all platforms and returns 0. The platform capability can be detected via QNetworkConfigurationManager::DataStatistics.
Definition at line 664 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkSessionPrivate::setALREnabled().
|
slot |
Decreases the session counter on the associated network configuration.
If the session counter reaches zero the active network interface is shut down. This also means that state() will only change from Connected to Disconnected if the current session was the last open session.
If the platform does not support out-of-process sessions calling this function does not stop the interface. In this case stop() has to be used to force a shut down. The platform capabilities can be detected via QNetworkConfigurationManager::capabilities().
Note that this call is asynchronous. Depending on the outcome of this call the results can be enquired by connecting to the stateChanged(), opened() or error() signals.
Definition at line 381 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkSessionPrivate::~QNetworkSessionPrivate().
|
signal |
This signal is emitted when the network session has been closed.
Referenced by QNetworkSession(), and QNetworkSessionPrivate::setPrivateConfiguration().
| QNetworkConfiguration QNetworkSession::configuration | ( | ) | const |
Returns the QNetworkConfiguration that this network session object is based on.
Definition at line 408 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkAccessManagerPrivate::_q_networkSessionClosed(), QNetworkAccessManager::configuration(), and QNetworkAccessBackend::start().
|
protectedvirtual |
This function is required to detect whether the client wants to control the roaming process.
If he connects to preferredConfigurationChanged() signal he intends to influence it. Otherwise QNetworkSession always roams without registering this session as a stakeholder in the roaming process.
For more details check the Forced vs ALR roaming section in the QNetworkSession class description.
Reimplemented from QObject.
Definition at line 710 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
|
protectedvirtual |
This function is called when the client disconnects from the preferredConfigurationChanged() signal.
Reimplemented from QObject.
Definition at line 734 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
| QNetworkSession::SessionError QNetworkSession::error | ( | ) | const |
Returns the type of error that last occurred.
Definition at line 470 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkSessionPrivateImpl::errorString(), open(), QNetworkSession(), and waitForOpened().
|
signal |
This signal is emitted after an error occurred.
The error parameter describes the error that occurred.
| QString QNetworkSession::errorString | ( | ) | const |
Returns a human-readable description of the last device error that occurred.
Definition at line 481 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
|
slot |
This function indicates that the application does not wish to roam the session.
Definition at line 614 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
| QNetworkInterface QNetworkSession::interface | ( | ) | const |
Returns the network interface that is used by this session.
This function only returns a valid QNetworkInterface when this session is Connected .
The returned interface may change as a result of a roaming process.
Note: this function does not work in Symbian emulator due to the way the connectivity is emulated on Windows.
Definition at line 426 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
| bool QNetworkSession::isOpen | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this session is open.
If the number of all open sessions is greater than zero the underlying network interface will remain connected/up.
The session can be controlled via open() and close().
Definition at line 438 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
|
slot |
Instructs the session to roam to the new access point.
The old access point remains active until the application calls accept().
The newConfigurationActivated() signal is emitted once roaming has been completed.
Definition at line 603 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkSessionPrivate::setALREnabled().
|
signal |
This signal is emitted once the session has roamed to the new access point.
The application may reopen its socket and test the suitability of the new network link. Subsequently it must either accept() or reject() the new access point.
Referenced by QNetworkSession(), and QNetworkSessionPrivate::setPrivateConfiguration().
|
slot |
Creates an open session which increases the session counter on the underlying network interface.
The system will not terminate a network interface until the session reference counter reaches zero. Therefore an open session allows an application to register its use of the interface.
As a result of calling open() the interface will be started if it is not connected/up yet. Some platforms may not provide support for out-of-process sessions. On such platforms the session counter ignores any sessions held by another process. The platform capabilities can be detected via QNetworkConfigurationManager::capabilities().
Note that this call is asynchronous. Depending on the outcome of this call the results can be enquired by connecting to the stateChanged(), opened() or error() signals.
It is not a requirement to open a session in order to monitor the underlying network interface.
Definition at line 316 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
|
signal |
This signal is emitted when the network session has been opened.
The underlying network interface will not be shut down as long as the session remains open. Note that this feature is dependent on system wide session support.
Referenced by QNetworkSession().
|
signal |
This signal is emitted when the preferred configuration/access point for the session changes.
Only sessions which are based on service network configurations may emit this signal. config can be used to determine access point specific details such as proxy settings and isSeamless indicates whether roaming will break the sessions IP address.
As a consequence to this signal the application must either start the roaming process by calling migrate() or choose to ignore() the new access point.
If the roaming process is non-seamless the IP address will change which means that a socket becomes invalid. However seamless mobility can ensure that the local IP address does not change. This is achieved by using a virtual IP address which is bound to the actual link address. During the roaming process the virtual address is attached to the new link address.
Some platforms may support the concept of Forced Roaming and Application Level Roaming (ALR). Forced roaming implies that the platform may simply roam to a new configuration without consulting applications. It is up to the application to detect the link layer loss and reestablish its sockets. In contrast ALR provides the opportunity to prevent the system from roaming. If this session is based on a configuration that supports roaming the application can choose whether it wants to be consulted (ALR use case) by connecting to this signal. For as long as this signal connection remains the session remains registered as a roaming stakeholder; otherwise roaming will be enforced by the platform.
Referenced by connectNotify(), disconnectNotify(), QNetworkSession(), and QNetworkSessionPrivate::setPrivateConfiguration().
|
slot |
The new access point is not suitable for the application.
By calling this function the session returns to the previous access point/configuration. This action may invalidate any socket that has been created via the not desired access point.
Definition at line 643 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkSessionPrivate::setALREnabled().
Returns the value for property key.
A network session can have properties attached which may describe the session in more details. This function can be used to gain access to those properties.
The following property keys are guaranteed to be specified on all platforms:
| Key | Description |
| ActiveConfiguration | If the session isOpen() this property returns the identifier of the QNetworkConfiguration that is used by this session; otherwise an empty string. The main purpose of this key is to determine which Internet access point is used if the session is based on a ServiceNetwork. The following code snippet highlights the difference: QNetworkConfiguration ap = mgr.defaultConfiguration(); ... //code activates session Q_ASSERT( ap.identifier() != ident ); Q_ASSERT( ap.identifier() == ident ); } |
| UserChoiceConfiguration | If the session isOpen() and is bound to a QNetworkConfiguration of type UserChoice, this property returns the identifier of the QNetworkConfiguration that the configuration resolved to when open() was called; otherwise an empty string. The purpose of this key is to determine the real QNetworkConfiguration that the session is using. This key is different from ActiveConfiguration in that this key may return an identifier for either a QNetworkConfiguration::ServiceNetwork{service network} or a QNetworkConfiguration::InternetAccessPoint{Internet access points} configurations, whereas ActiveConfiguration always returns identifiers to QNetworkConfiguration::InternetAccessPoint{Internet access points} configurations. |
| ConnectInBackground | Setting this property to true before calling open() implies that the connection attempt is made but if no connection can be established, the user is not connsulted and asked to select a suitable connection. This property is not set by default and support for it depends on the platform. |
| AutoCloseSessionTimeout | If the session requires polling to keep its state up to date, this property holds the timeout in milliseconds before the session will automatically close. If the value of this property is -1 the session will not automatically close. This property is set to -1 by default. The purpose of this property is to minimize resource use on platforms that use polling to update the state of the session. Applications can set the value of this property to the desired timeout before the session is closed. In response to the closed() signal the network session should be deleted to ensure that all polling is stopped. The session can then be recreated once it is required again. This property has no effect for sessions that do not require polling. |
Definition at line 553 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkAccessBackend::start(), and QNetworkSessionPrivate::~QNetworkSessionPrivate().
Sets the property value on the session.
The property is identified using key. Removing an already set property can be achieved by passing an invalid QVariant.
Note that the UserChoiceConfiguration and ActiveConfiguration properties are read only and cannot be changed using this method.
Definition at line 582 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkSessionPrivate::~QNetworkSessionPrivate().
| QNetworkSession::State QNetworkSession::state | ( | ) | const |
Returns the state of the session.
If the session is based on a single access point configuration the state of the session is the same as the state of the associated network interface. Therefore a network session object can be used to monitor network interfaces.
A QNetworkConfiguration::ServiceNetwork based session summarizes the state of all its children and therefore returns the Connected state if at least one of the service network's QNetworkConfiguration::children(){children()} configurations is active.
Note that it is not required to hold an open session in order to obtain the network interface state. A connected but closed session may be used to monitor network interfaces whereas an open and connected session object may prevent the network interface from being shut down.
Definition at line 460 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkReplyImplPrivate::_q_networkSessionConnected(), and QNetworkSessionPrivate::setPrivateConfiguration().
|
signal |
This signal is emitted whenever the state of the network session changes.
The state parameter is the new state.
Referenced by QNetworkSession(), and QNetworkSessionPrivate::setPrivateConfiguration().
|
slot |
Invalidates all open sessions against the network interface and therefore stops the underlying network interface.
This function always changes the session's state() flag to Disconnected .
On Symbian platform, a 'NetworkControl' capability is required for full interface-level stop (without the capability, only the current session is stopped).
Definition at line 397 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
Referenced by QNetworkSessionPrivate::~QNetworkSessionPrivate().
| bool QNetworkSession::waitForOpened | ( | int | msecs = 30000 | ) |
Waits until the session has been opened, up to msecs milliseconds.
If the session has been opened, this function returns true; otherwise it returns false. In the case where it returns false, you can call error() to determine the cause of the error.
The following example waits up to one second for the session to be opened:
If msecs is -1, this function will not time out.
Definition at line 341 of file qnetworksession.cpp.
|
friend |
Definition at line 139 of file qnetworksession.h.
|
private |
Definition at line 140 of file qnetworksession.h.
Referenced by accept(), activeTime(), bytesReceived(), bytesWritten(), close(), configuration(), connectNotify(), disconnectNotify(), error(), errorString(), ignore(), interface(), isOpen(), migrate(), open(), QNetworkSession(), reject(), sessionProperty(), setSessionProperty(), state(), stop(), waitForOpened(), and ~QNetworkSession().